The Sim Smithy is currently in Private Beta. We are accepting applications for three 'Pilot Partners' for Q1 2026 deployment. [Enquire for Availability]
Real World Challenges. Simulated
Browse our examples of bespoke simulations. Each was built by The Sim Smithy framework and assessed by separate AI models.
// AI Assessment: Claude
BrightBank: Building the Future
Banking & Capital | Audience: Graduate Intake
The Brief
A UK retail bank faced a persistent challenge with its graduate intake: while academically qualified, new hires struggled to grasp the holistic operations of a bank outside their silos. Traditional training on concepts like Net Interest Margin (NIM) and capital ratios provided theory but failed to convey the visceral difficulty of strategic trade-offs.
The Goal: The stakeholder required a clear behavioral shift: graduates needed to instinctively ask, “What does this decision do to our NIM, capital position, and cost-to-income ratio?”
Key Objectives: Understanding Banking Economics, Regulatory Reality, Channel Strategy, and Systems Thinking.
The Solution & Mechanics
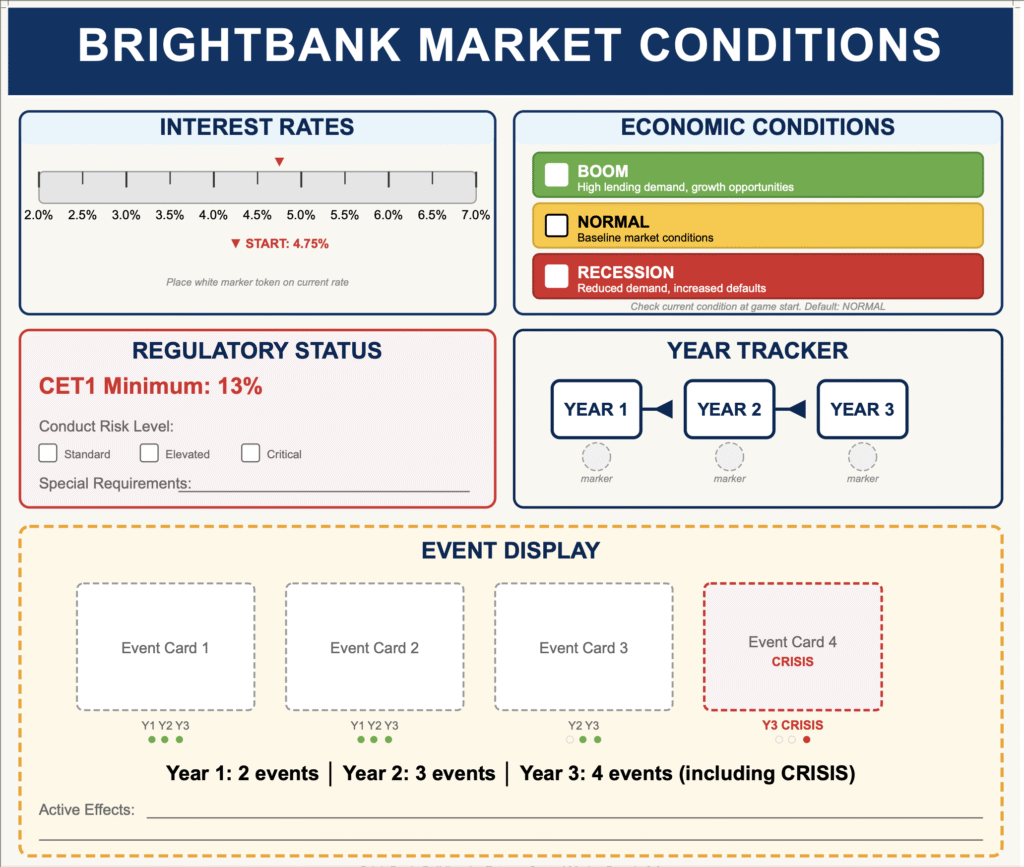
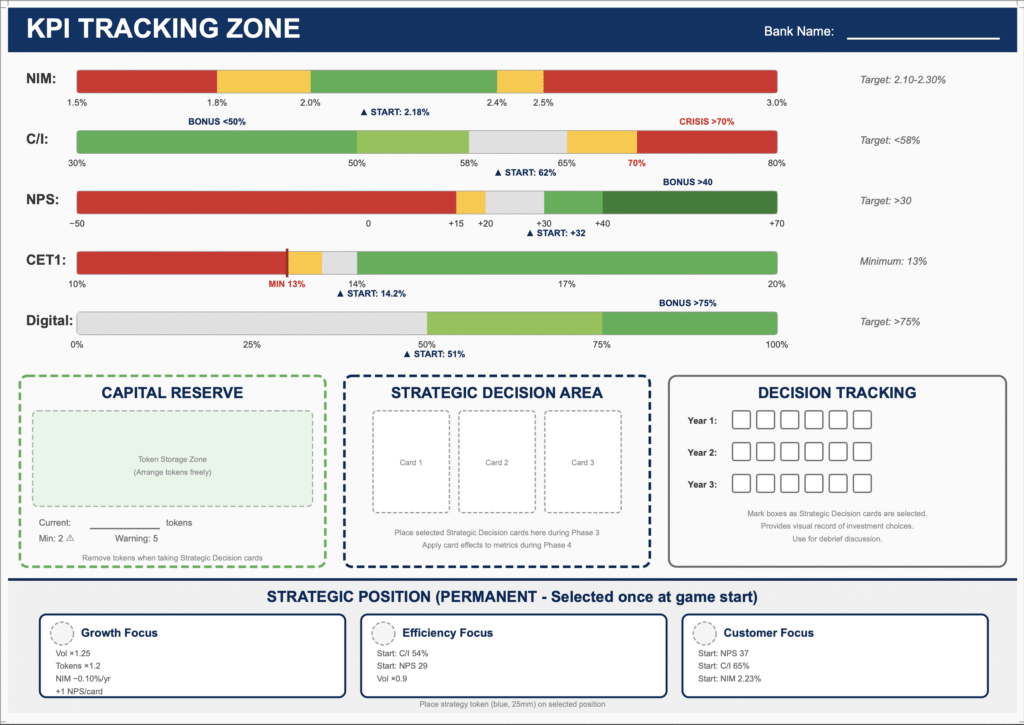
Teams take control of BrightBank, a mid-sized UK retail bank with £68 billion in assets. Over three simulated years, they navigate market shocks and manage five interconnected KPIs on a physical dashboard.
Core Mechanic: Physical Capital Constraint To solve the issue of “abstract” regulation, the simulation uses physical capital tokens. Each team has 30 tokens (representing £3bn regulatory capital). If tokens run out, they cannot lend. This transforms a dry compliance rule into an immediate, physical limitation that shapes every discussion.
Secondary Feature: Dynamic Market Events A deck of 24 event cards introduces external shocks—interest rate hikes, competitor moves, and a guaranteed Year 3 crisis. All teams face identical events but respond independently, allowing for rich comparative debriefs.
Visual Components
Team Dashboard: Tracks NIM, Cost-to-Income, and Capital Ratio with color-coded scales for immediate feedback.
Central Market Board: Displays the shared economic climate (Boom/Recession) and current interest rates.
AI Assessment & Specs
Assessment (Vetted by Claude)
Alignment with Learning Objectives: The physical token system successfully addresses the brief’s requirement for graduates to “feel” constraints rather than just calculate them. The five tracked metrics (NIM, Cost-to-Income, etc.) map precisely to the banking fundamentals identified as essential learning. The strategic positions create genuinely differentiated pathways, ensuring no single “winning” strategy exists.
Facilitation Design: The design enables general L&D professionals to run the session without specialist banking knowledge , thanks to the comprehensive manual and 15-minute banking primer.
Summary Specifications
Duration: 4 hours (Half-day)
Participants: 12–16 (4 teams of 3–4)
Complexity: Medium-High (Graduate level)
Physical Components: Capital tokens, team dashboards, central market board, decision cards, event cards
Facilitator Requirement: L&D professional with moderate facilitation experience
// AI Assessment: Claude
RiskWise: Building a Profitable Portfolio
Insurance & Risk | Audience: Underwriters & Portfolio Managers
The Brief
A UK commercial insurer identified a dangerous blind spot in their underwriting teams: while technically proficient at pricing individual risks, they struggled to see portfolio-level exposure. They were writing “good business” in isolation that became toxic in aggregate due to concentration risk.
The Goal: The stakeholder needed to shift the mindset from “transactional pricing” to “portfolio construction.” The simulation had to force participants to stop asking “Is this a good risk?” and start asking “What does this risk do to our capital adequacy and concentration limits?”
The Solution & Mechanics
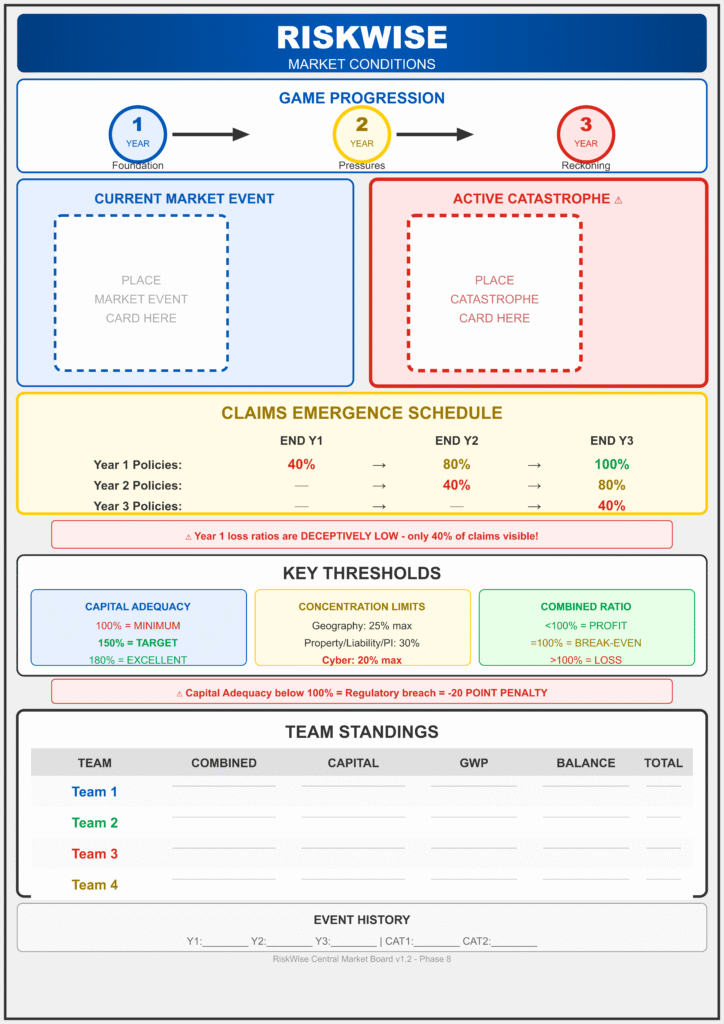
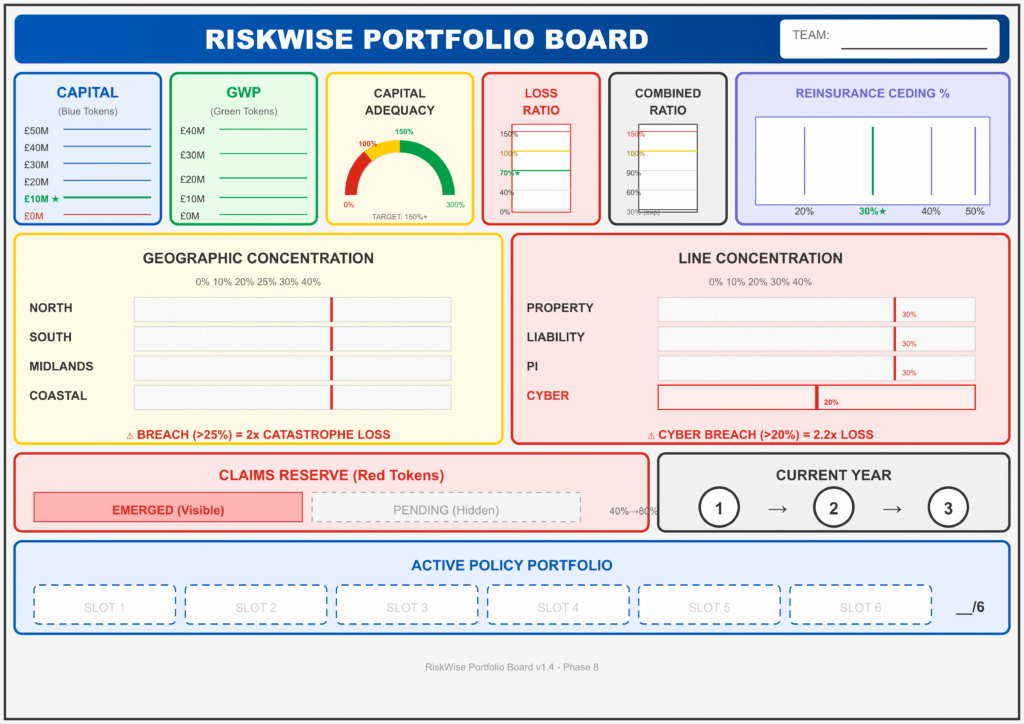
Teams take control of a mid-sized commercial insurer over a three-year simulated period. They must balance growth against capital constraints, managing a portfolio across eight distinct dimensions (including Geography and Line of Business).
Core Mechanic: The Trap of Delayed Emergence In insurance, premiums are paid today, but claims happen tomorrow. The simulation models this perfectly: only 40% of claims emerge in Year 1. This tempts teams into aggressive, under-priced growth that looks profitable initially—until Years 2 and 3, when the “long tail” of claims destroys their capital.
Key Feature: The Concentration Penalty Diversification is enforced mechanically. If a team exceeds 25% exposure in any single region or line of business, the simulation triggers a “Concentration Multiplier.” When a catastrophe card (like a Flood or Cyber Attack) is drawn, these teams suffer double losses, turning a manageable event into a solvency crisis.
AI Assessment & Specs
Assessment (Vetted by Claude)
Fidelity to Reality: The assessment highlights the “Delayed Claims Emergence” mechanic as a critical learning tool, validating that it successfully replicates the “Year 1 deception” that traps new underwriters.
Strategic Depth: The “Reinsurance Slider” (balancing profit retention vs. protection) was praised for creating meaningful strategic trade-offs rather than being a simple math problem.
Behavioral Impact: The “Physical Capital Constraints” (blue tokens) effectively force teams to experience regulatory limits as a hard operational wall, not just a compliance checkbox.
Summary Specifications
Duration: 4 Hours (Half-day)
Participants: 12–16 (4 teams)
Complexity: Intermediate-Advanced (Professional Level)
Facilitator: L&D Professional (Insurance expertise helpful but not mandatory)
// AI Assessment: Claude
Project Fusion: The Tech Services Challenge
Tech Services | Audience: Sales Leads, Project Managers, & Delivery Teams
The Brief
A global technology consultancy faced a disconnect between their Sales and Delivery functions. Sales teams were “throwing deals over the fence,” winning contracts that were impossible to deliver profitably, while Delivery teams struggled to articulate the commercial impact of scope creep.
The Goal: The firm needed to instill “Commercial Acumen” in new hires, moving them from technical thinking to commercial thinking. The simulation had to force participants to experience the entire “Bid-to-Delivery” lifecycle, realizing that a signed contract is a liability, not an asset, until it is delivered.
The Solution & Mechanics
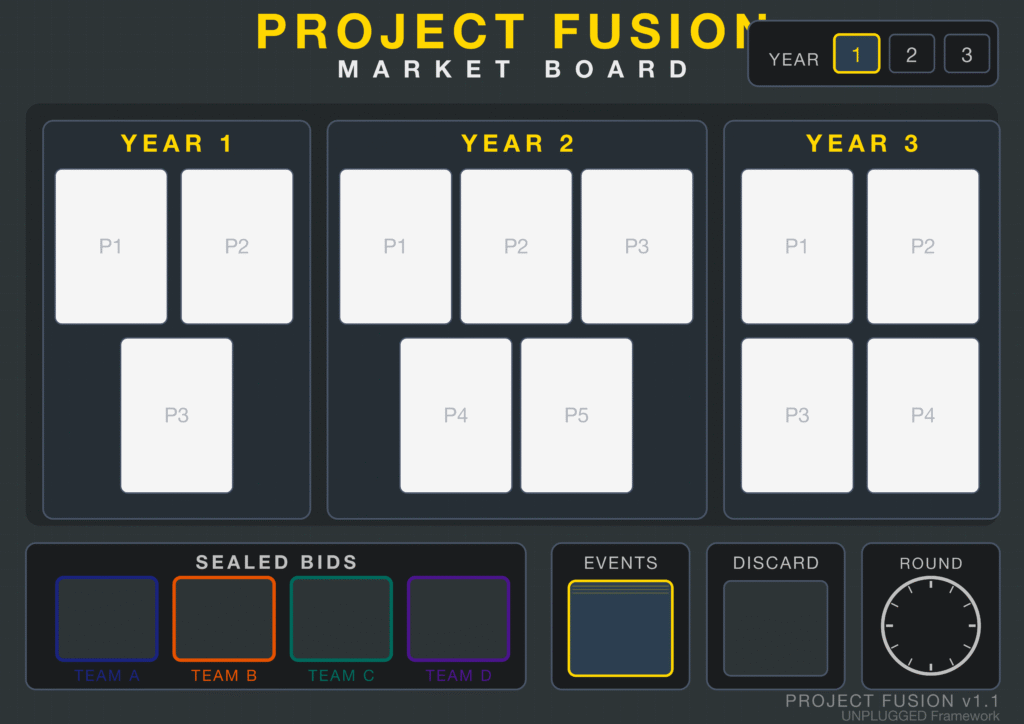
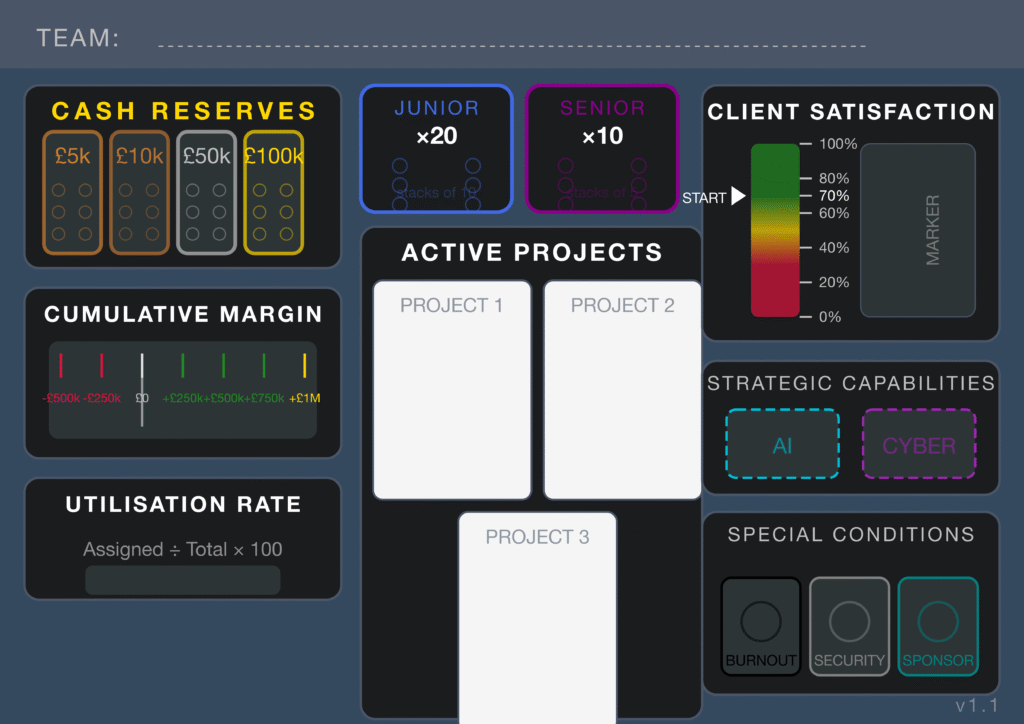
Teams run competing tech consultancies, managing a bench of physical Junior and Senior Consultant tokens. They must navigate the tension between winning work in the Market Phase and executing it in the Delivery Phase, all while managing Utilisation Rates and Client Satisfaction.
Core Mechanic: The Bid-to-Delivery Lifecycle. The game strictly separates “Winning” from “Doing.” Teams who over-promise in the bidding war face an immediate resource crisis in the delivery phase. If you bid for a massive integration project but your Senior Consultants are already committed, you default on the contract—damaging your reputation permanently.
Key Feature: The Utilization Trap. Profit requires keeping staff busy (billable), but 100% utilization leaves no slack for crises. Teams must balance the “Bench Cost” of idle staff against the “Burnout Risk” of overworking them.
Strategic Capabilities: As the game progresses, teams can invest cash reserves to unlock AI and Cyber capabilities, allowing them to bid on higher-margin “Specialty Projects” in Year 3—but only if they survived the cash-flow pressure of Year 1.
AI Assessment & Specs
Assessment (Vetted by Gemini)
Final Rating: 94/100 (“Masterclass in simulation design”)
Behavioral Shift: The assessment notes the simulation successfully engineers the shift from “technical” to “commercial” thinking. By assigning conflicting role cards (Sales asks “Can we win?”, Commercial asks “What’s the margin?”), the design “organically generates the cross-functional debate” requested in the brief.
Tangible Scarcity: Gemini highlighted the use of physical tokens as a design highlight: “It transforms abstract numbers into visceral limitations—when a team runs out of blue ‘Junior Consultant’ tokens, the capacity crisis is immediately visible and felt.”
Summary Specifications
Duration: 3 Hours
Participants: 20 (4 Teams of 5)
Complexity: Medium (Physical Economy + Card System)
Facilitator: General Trainer (Detailed Scripting provided for “Analysis Paralysis” troubleshooting)
// AI Assessment: Gemini
UrbanEdge: The First Three Years
Retail Strategy | Audience: New Hires & Future Leaders
The Brief
A fast-growing sustainable fashion retailer identified a critical gap: new hires arrived with deep functional expertise but lacked a holistic view of the business. This led to siloed decision-making—optimizing individual departments while harming the overall strategy.
The Goal: The project required a behavioural shift. New hires needed to transition from functional specialists to strategic thinkers who instinctively ask: “How does this initiative support our core strategy and what is the impact on Gross Margin?”.
The Solution & Mechanics
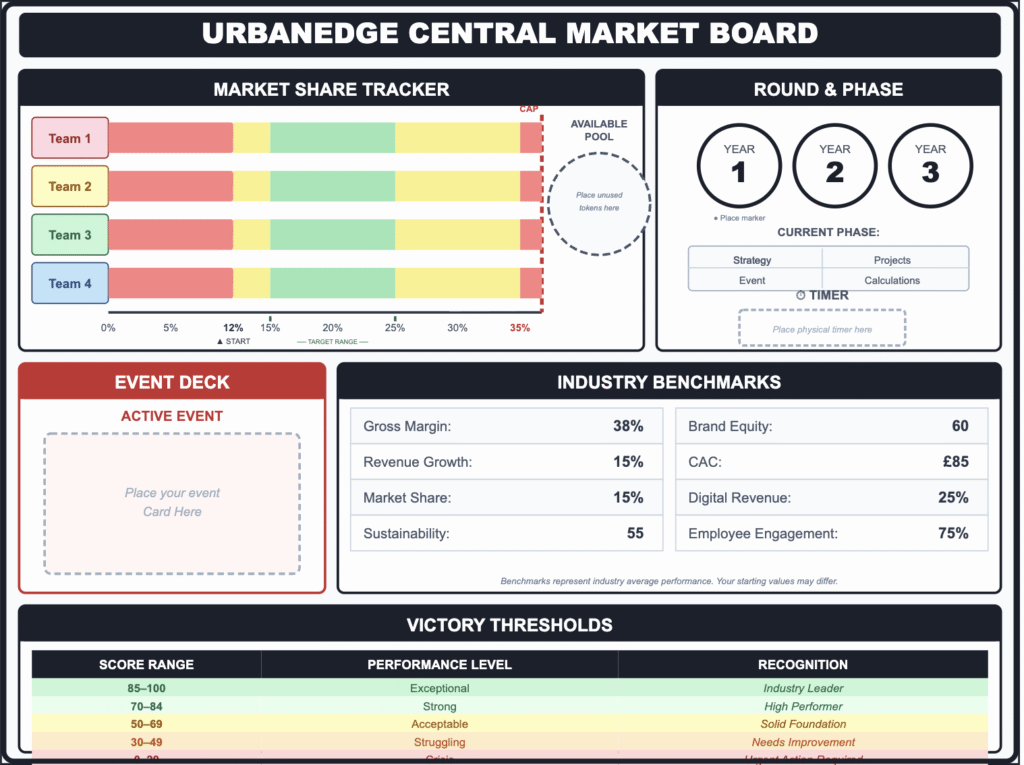
Four competing teams take control of UrbanEdge for a simulated three-year period. They operate with full transparency, managing resources to build market share while adhering to strict sustainability goals.
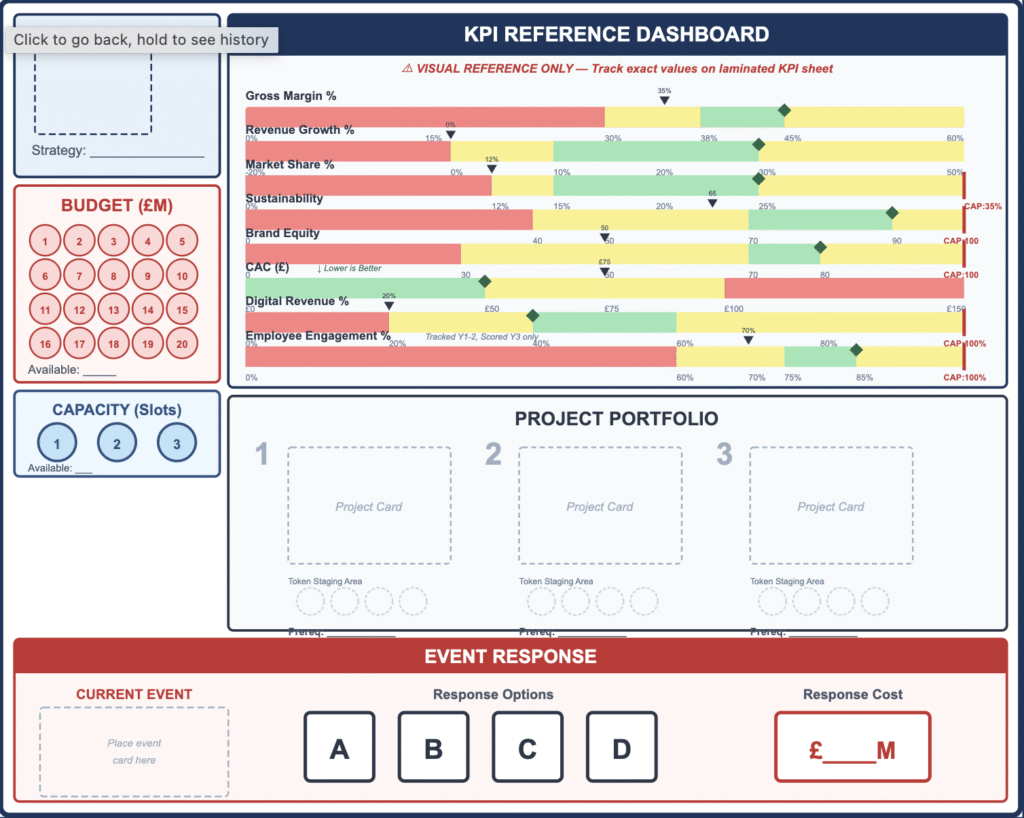
Core Mechanic: Dual-Resource Economy Teams manage two finite currencies: Budget Tokens (Capital) and Capacity Tokens (Time/Focus). They must allocate these across 5–7 strategic projects per year. This forces an immediate trade-off: high-impact sustainability projects often consume the capacity needed for market expansion.
Secondary Feature: Strategic Pillars In Year 1, teams commit to a pillar (e.g., Innovation or Brand Strength). This creates “strategic lock-in,” ensuring Year 3 decisions must be evaluated against Year 1 commitments rather than in isolation.
AI Assessment & Specs
Assessment (Vetted by Gemini)
Breaking Silos: By removing role differentiation and forcing the entire team to agree on a unified strategy, the design effectively eliminates functional isolation.
Tangible Trade-offs: The simulation operationalizes the “Sustainability vs. Margin” tension mechanically—ethical materials explicitly cost 30–50% more, forcing teams to feel the cost of their values.
Data-Driven: The requirement to use financial data to justify strategy directly addresses the “observable success behaviour” requested in the brief.
Summary Specifications
- Duration: 5 hours (including debrief)
- Participants: 16 (4 teams of 4)
- Complexity: Entry to Mid-Level
- Physical Components: 4 Team Boards, 21 Project Cards, Capital & Capacity Tokens
// AI Assessment: Gemini
Response Ready: The Dual Mandate
Public Sector | Audience: Project Managers & Executives
The Brief
A national protection agency identified a critical mindset gap in their Project Executives. While excellent at delivering planned infrastructure projects (“Planned Surgery”), they treated emergency incidents as frustrating “interruptions” rather than their primary duty.
The Goal: The stakeholder needed to reframe the operating model. The simulation had to force Project Managers to master the “Mode Switch”—instantly pivoting from rigid Gateway governance to high-stakes incident response—without neglecting the strict audit trails required by government spending rules.
The Solution & Mechanics
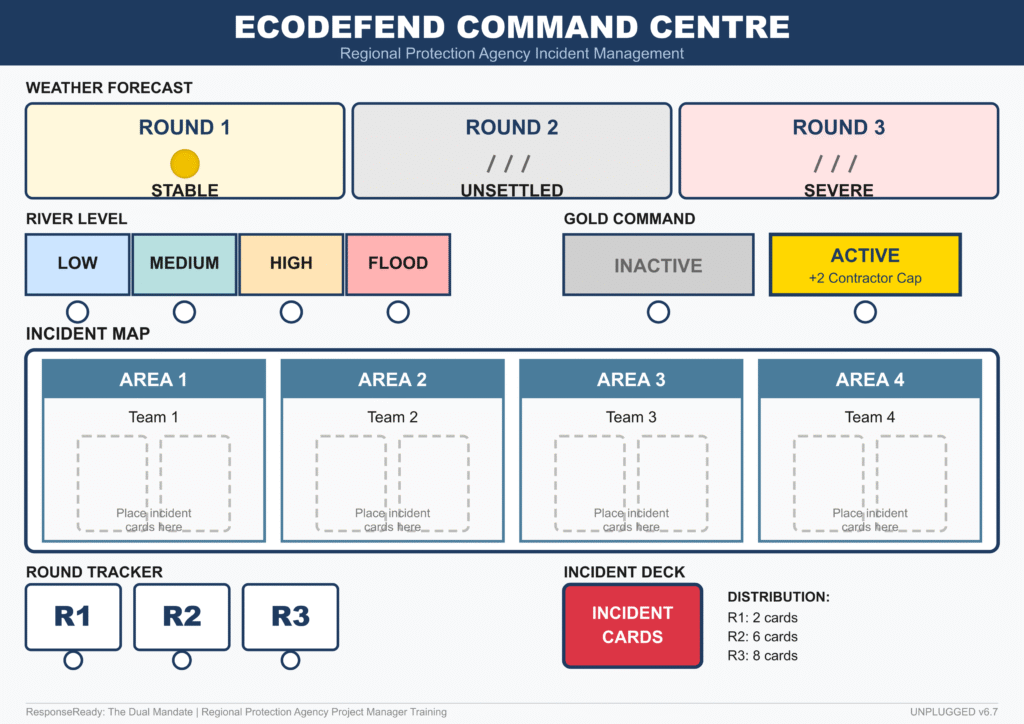
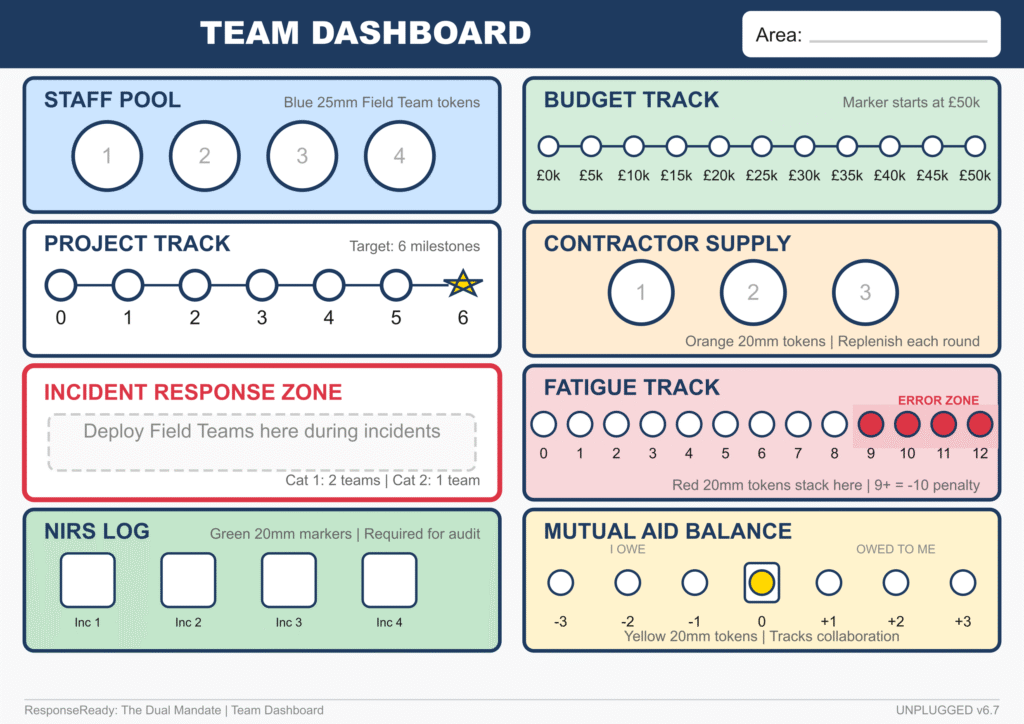
Teams manage a portfolio of capital projects (managing Business Cases and Gateway Reviews) while simultaneously staffing an Incident Response rota. They must balance the “Iron Triangle” of project delivery against the unpredictable demands of Gold Command escalations.
Core Mechanic: The Interrupt System. Incidents are not scheduled—they physically interrupt play. When a “Category 1” event hits, teams must physically halt their Business Case review, stop the timer, and redeploy their limited Staff Pool to the Incident Response Zone. This visceral “Mode Switch” makes the trade-off between project delivery and public safety impossible to ignore.
Key Feature: Compliance Debt (The NIRS Log). In the heat of a crisis, teams are tempted to skip the paperwork to “get the job done.” The simulation tracks this via the NIRS Log (National Incident Recording System). If teams fail to log decisions, “Compliance Debt” accumulates quietly—only to detonate during the Round 3 Audit, proving the painful lesson: “If it’s not in the system, it didn’t happen.”
The Fatigue Track: Over-using staff without rest pushes them into the Error Zone on the Fatigue Track, forcing players to make difficult ethical choices between burning out their team or missing a deadline.
AI Assessment & Specs
Assessment (Vetted by ChatGPT)
Fidelity to Reality: The assessment confirms the simulation “mirrors the real-world collision between ‘planned surgery’ and ’emergency room’ work exactly as specified,” successfully operationalizing the agency’s “Dual Mandate”.
Behavioral Impact: The reviewer noted that the “Ruthless Triage” logic is deeply embedded. Teams quickly learn that “doing nothing is often the correct operational choice” for low-priority incidents, effectively curing the tendency to over-respond to noise.
Structural Integrity: The simulation “exceeds requirements” on facilitation support, with the AI noting that the specific “Compliance Debt” mechanic transforms abstract bureaucracy into a genuine tactical pressure.
Summary Specifications
Duration: 4 Hours (Half-day format)
Participants: 12-16 (Flexible Team Structures)
Complexity: Intermediate-Advanced (Public Sector / Governance Focus)
Facilitator: L&D Professional (Subject Matter Expertise not required due to script depth)
// AI Assessment: ChatGPT
A&E Control Scenario: The First Year
Healthcare Leadership | Audience: Clinical & Operational Leads
The Brief
A fictitious NHS Trust identified a critical gap in its leadership pipeline: newly appointed Emergency Department managers understood the language of safety and targets, but not the lived tension between them. They tended to chase the 95% 4-hour waiting standard reactively, often at the expense of clinical quality and staff wellbeing.
The Goal: The simulation needed to drive a specific behavioral shift. Under pressure, managers should stop asking “How do we hit the target?” and start asking “What is the impact of this decision on safety, staff sustainability, and system constraints?” .
The Solution & Mechanics
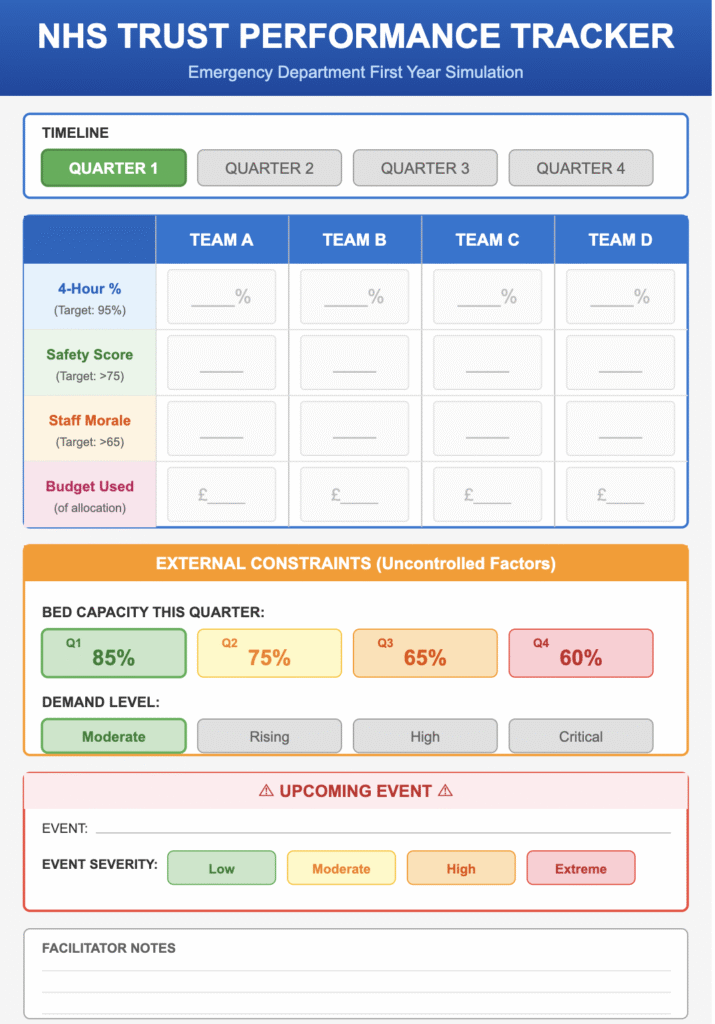
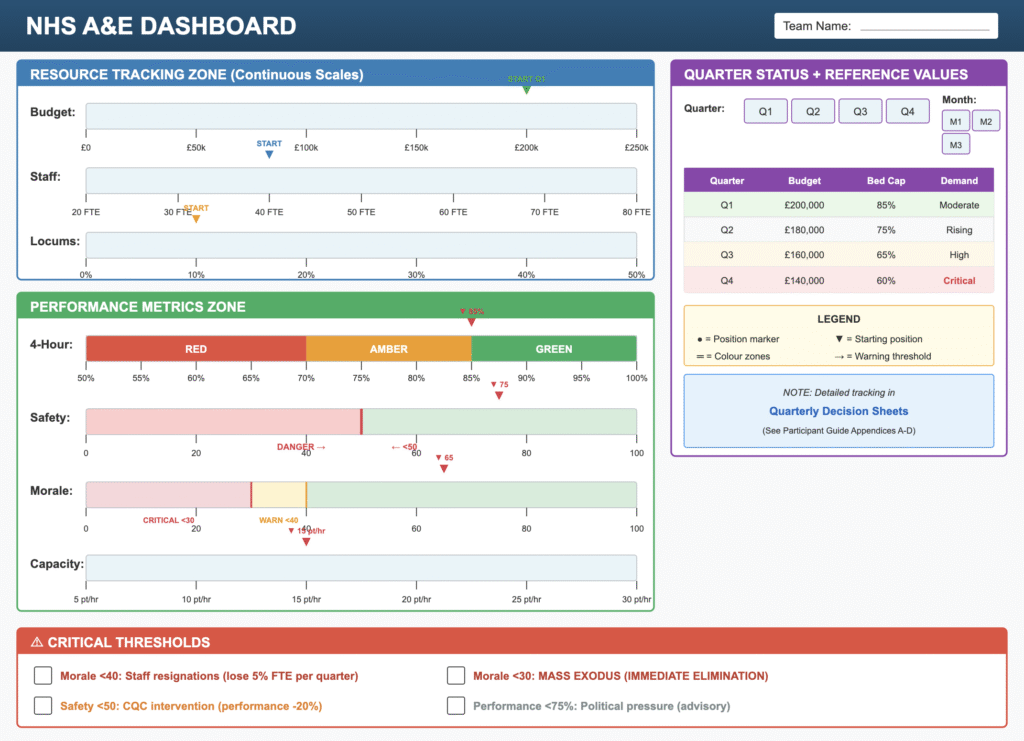
Teams manage a single NHS Emergency Department through four quarters of operation. They face identical external pressures—flu spikes, recruitment delays, and bed block—but make independent decisions on staffing, pathways, and crisis response.
Core Mechanic: The Triangle of Impossibility The simulation models an explicit three-way tension between 4-Hour Performance, Clinical Safety, and Staff Morale . Every “fix” has a cost. For example, opening a “Fast-Track Pathway” boosts performance but reduces safety oversight. Relying on agency locums increases capacity but destroys the budget and staff morale.
Secondary Feature: Cascade Thresholds Failure is meaningful. If Morale drops too low, staff resign (reducing capacity further). If Safety drops, the CQC intervenes. This forces participants to balance short-term survival against long-term collapse.
AI Assessment & Specs
Assessment (Vetted by ChatGPT)
- Alignment with Learning Objectives: The simulation shows strong fidelity to the brief. The “Triangle of Impossibility” ensures the core tension (Targets vs. Safety) is mechanically unavoidable.
- Systemic Thinking: Whole-hospital flow and bed capacity are treated as dominant external constraints, forcing teams to realize that ED performance cannot be fixed solely within the ED.
- Facilitation: The materials exceed expectations for generalist trainers, providing detailed scripts that translate mechanical outcomes (like a safety breach) into realistic NHS scenarios
Summary Specifications
- Duration: 3.5 hours (including debrief)
- Participants: 12–16 (4 teams of 3–4)
- Complexity: Intermediate-Advanced
- Physical Components: Team dashboards, master tracking board, decision cards, event cards, tokens
- Facilitator: L&D professional (NHS expertise helpful but not mandatory)
Stop waiting months...
Let’s discuss your specific learning objectives…
